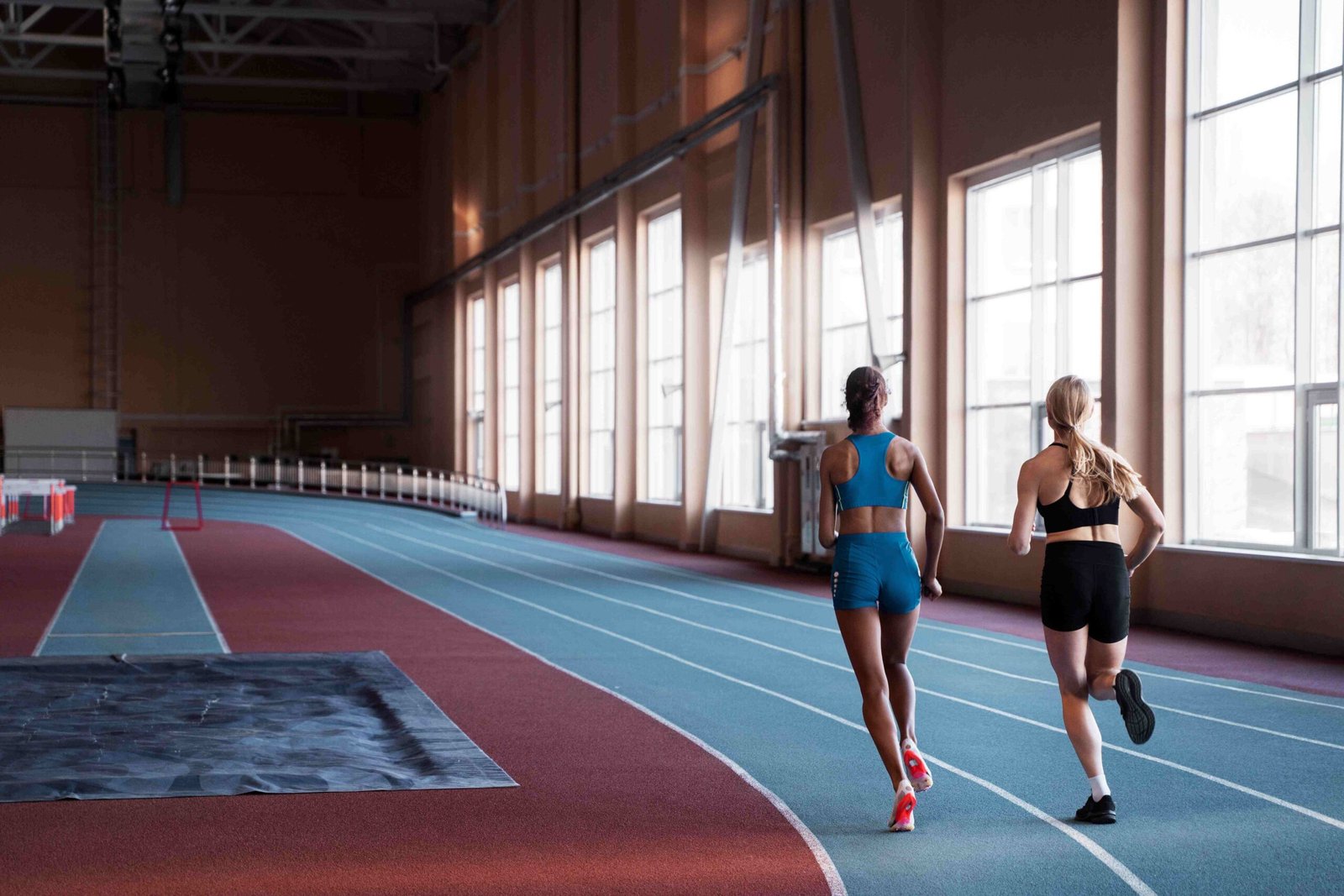
When it comes to indoor sports flooring, cushioning alone is not enough. Facility managers, coaches, and athletes increasingly ask:
“Beyond basic cushioning, what are the specific performance metrics (like force reduction) that confirm this floor is optimized for athletic performance and safety?”
Sports flooring must not only feel comfortable underfoot but also enhance athletic performance, protect joints, and provide a consistent surface for all types of indoor sports. Two critical metrics—force reduction and vertical deformation—are key indicators of how a floor performs under dynamic loads. Understanding these metrics helps decision-makers select flooring that balances safety, durability, and performance.
This comprehensive guide explores the science behind these metrics, how they impact athletic safety and performance, international standards, flooring materials, and best practices for selecting high-performing sports surfaces.
Understanding Force Reduction
Force reduction measures the floor’s ability to absorb impact forces generated during sports activities. When athletes jump, land, or sprint, the floor absorbs some of the energy, reducing the stress transferred to their joints.
1. Why Force Reduction Matters
- Injury Prevention: High-impact movements can lead to ankle sprains, knee ligament injuries, and lower back stress. A floor with optimal force reduction mitigates these risks.
- Athletic Comfort: Proper force absorption allows athletes to train longer and perform better without fatigue.
- Performance Consistency: Consistent energy absorption ensures predictable movement and balance, critical for sports like basketball, volleyball, and badminton.
2. Measuring Force Reduction
Force reduction is quantified as a percentage of impact absorbed by the floor. For example:
- A force reduction of 35% means the floor absorbs 35% of the impact, while 65% is transmitted to the athlete.
- Lower percentages (<25%) may be too rigid, increasing joint stress.
- Excessive force reduction (>50%) may feel “mushy” and reduce energy return for jumps and sprints.
Testing Standards:
- EN 14808: European standard for shock absorption testing of sports floors.
- FIBA & BWF Guidelines: Define acceptable ranges for professional basketball and badminton floors.
Understanding Vertical Deformation
Vertical deformation refers to the amount a floor compresses under a vertical load, such as a player landing from a jump. It indicates how much the surface “gives” under pressure.
1. Why Vertical Deformation Matters
- Joint Protection: Proper deformation reduces impact stress on ankles, knees, and hips.
- Energy Return: Surfaces with controlled deformation provide a balance between shock absorption and energy return, enhancing jump height and agility.
- Consistency: Uniform vertical deformation ensures predictable footing and ball bounce.
2. Measuring Vertical Deformation
- Measured in millimeters (mm) under a standard load (often 50–60 kg for testing).
- Recommended ranges vary by sport:
- Basketball: 2–4 mm
- Volleyball: 2–3 mm
- Badminton/Table Tennis: 1.5–3 mm
- Basketball: 2–4 mm
Testing Standards:
- EN 14809: Measures vertical deformation for sports flooring.
- ASTM F2772: Provides protocols for impact testing in North America.
How Force Reduction and Vertical Deformation Affect Athlete Safety
1. Reduced Joint Stress
- Proper absorption prevents repetitive stress injuries.
- Supports high-impact training without long-term damage.
2. Enhanced Agility and Performance
- Balanced energy return allows for faster cuts, sprints, and jumps.
- Predictable deformation ensures reliable traction and ball behavior.
3. Fatigue Management
- Surfaces that absorb shock effectively reduce muscular fatigue.
- Athletes can perform at peak levels for longer periods.
4. Prevention of Chronic Injuries
- Continuous exposure to hard surfaces contributes to conditions like shin splints, knee pain, and plantar fasciitis.
- Optimized floors mitigate these risks, especially in high-volume training facilities.
Flooring Materials and Their Impact on Performance
Different sports flooring materials achieve force reduction and vertical deformation differently.
1. Hardwood Flooring
- Force Reduction: Typically 30–35% with engineered subfloor systems.
- Vertical Deformation: 2–4 mm depending on underlayment.
- Benefits: Natural rebound and energy return; professional feel for basketball.
- Considerations: Sensitive to moisture; requires climate control for consistent performance.
2. Vinyl Sports Flooring
- Force Reduction: 25–40% depending on padding and layers.
- Vertical Deformation: 1.5–3 mm with reinforced backing.
- Benefits: Consistent shock absorption; low maintenance; moisture resistant.
- Considerations: Lower energy return compared to hardwood but safer for schools and gyms.
3. Polyurethane / Synthetic Flooring
- Force Reduction: 30–45% with seamless application.
- Vertical Deformation: 2–3 mm controlled by material composition.
- Benefits: Excellent shock absorption; smooth and uniform surface; long lifespan.
- Considerations: Requires professional installation for optimal performance.
4. Rubber Flooring
- Force Reduction: 35–50% depending on thickness and density.
- Vertical Deformation: 2–5 mm; ideal for weight training areas.
- Benefits: High durability and impact resistance; easy to maintain.
- Considerations: Less suitable for ball sports due to altered rebound.
Subfloor Considerations for Optimal Performance
The subfloor plays a crucial role in achieving desired force reduction and vertical deformation:
- Floating Subfloors:
- Provide added cushioning and energy absorption.
- Common in professional basketball courts and high-performance volleyball halls.
- Provide added cushioning and energy absorption.
- Moisture-Resistant Concrete:
- Essential for vinyl and polyurethane floors.
- Maintains consistent deformation without swelling or warping.
- Essential for vinyl and polyurethane floors.
- Shock Pads and Underlays:
- Enhance force reduction and comfort.
- Can be engineered to meet specific vertical deformation standards.
- Enhance force reduction and comfort.
- Structural Integrity:
- Joists and support beams must handle dynamic loads without sagging.
- Subfloor strength directly impacts safety and performance.
Testing and Certification
High-performance sports floors are tested under realistic athletic conditions to validate safety metrics.
- Shock Absorption Testing (EN 14808): Measures the percentage of impact energy absorbed.
- Vertical Deformation Testing (EN 14809): Ensures compression under standard loads is within safe limits.
- Ball Rebound Testing: Confirms consistent bounce and surface uniformity.
- Certification by Sports Federations: FIBA, BWF, ITTF certifications ensure floors meet professional standards.
These tests provide facility managers with data-backed assurance of floor performance.
Installation and Maintenance Impact
Proper installation and maintenance directly influence force reduction and vertical deformation:
- Improper Adhesion or Loose Panels: Reduces shock absorption and causes uneven deformation.
- Subfloor Irregularities: Lead to inconsistent performance and potential safety hazards.
- Neglecting Maintenance: Dirt, moisture, and wear reduce force reduction efficiency over time.
Ensuring professional installation and routine care preserves the designed performance metrics of the floor.
Choosing the Right Floor for Sports Performance
When selecting a sports floor, consider:
- Intended Sports Use: Basketball, volleyball, badminton, and table tennis have different optimal ranges for force reduction and vertical deformation.
- Athlete Safety: Look for certified floors with verified shock absorption and deformation metrics.
- Material Composition: Multi-layer vinyl, hardwood with engineered subfloors, or polyurethane systems can provide tailored performance.
- Budget and Maintenance: High-performance floors may require higher initial investment but save costs in injury prevention and long-term durability.
Real-World Applications
- Professional Basketball Courts: Hardwood with floating subfloors engineered for 35% force reduction and 3 mm vertical deformation ensures elite player performance.
- School Gyms: Vinyl flooring with reinforced backing provides safe cushioning for youth athletes, reducing risk of injury.
- Community Volleyball Halls: Polyurethane seamless flooring delivers consistent rebound and shock absorption for multi-sport use.
- Fitness Centers: Rubber floors absorb high impact from weights and jumping exercises while maintaining vertical stability.
Conclusion
Force reduction and vertical deformation are more than technical specifications—they are indicators of athlete safety, performance optimization, and facility longevity.
- Floors with proper force reduction minimize stress on joints, prevent fatigue, and reduce injuries.
- Floors with controlled vertical deformation ensure predictable footing, energy return, and uniform ball bounce.
- Material choice, subfloor preparation, professional installation, and ongoing maintenance are all essential to maintaining these metrics.
- Certification by recognized organizations like FIBA, BWF, and EN standards provides assurance that the flooring meets stringent athletic performance criteria.
By understanding and prioritizing these metrics, facility managers, schools, and gym owners can make informed decisions that enhance athlete safety, improve performance, and protect long-term investment.
Ultimately, a high-performing sports floor is one that combines optimal force reduction, precise vertical deformation, durability, and consistent maintenance—creating an environment where athletes can train and compete at their best.